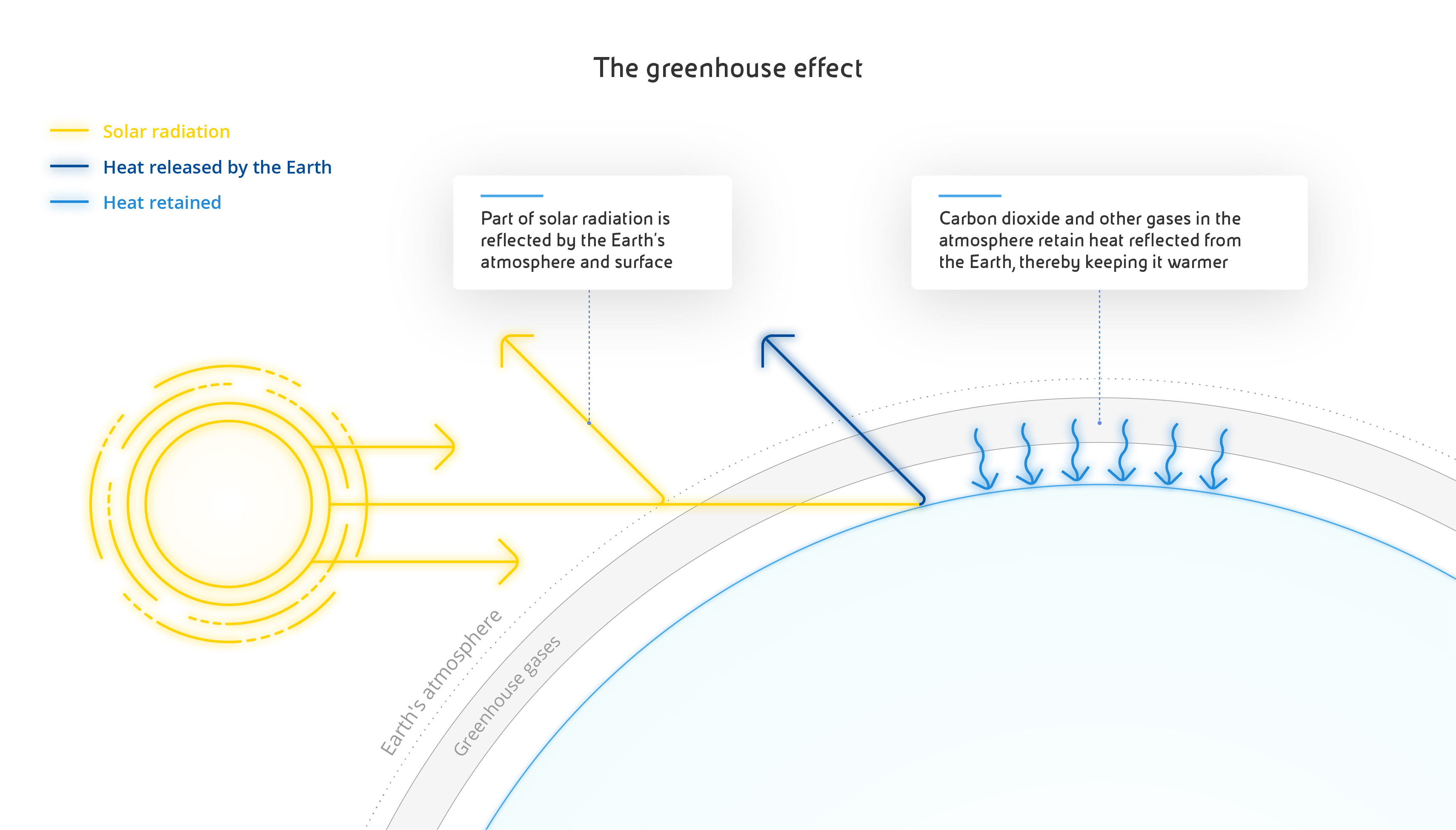
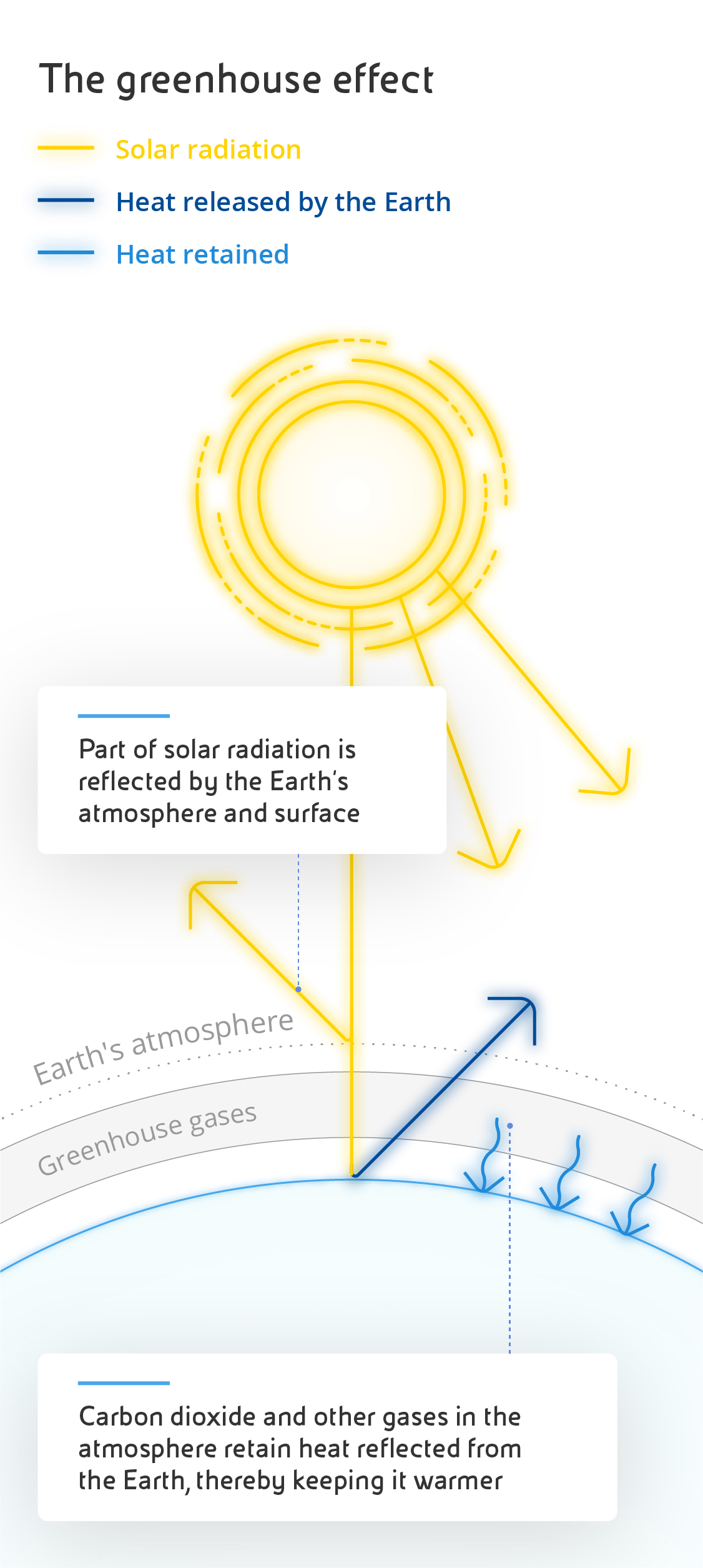
Carbon dioxide is made up of two oxygen atoms paired with a single carbon atom, chemically represented as CO₂. Occurring naturally in its gaseous form, it is essential to life on earth because of its central role in the carbon cycle - a series of complex chemical processes that govern the metabolism of every organism on the planet. Put simply, living organisms release CO₂ during respiration and terrestrial plants and marine phytoplankton use it for photosynthesis, then it returns to animals through food intake and digestion. The average concentration of CO₂ in our atmosphere is 0.04%. Another of its crucial roles is to create the greenhouse effect, a natural process that traps a portion of the sun's heat on the surface of our planet, ensuring that temperatures are suitable to life, as happens in greenhouses during the winter. Without CO₂, the earth's surface would be much colder and there would be no vegetation at all.
Our Channels
enioilproducts
Your business, our energy
Produtcs and solutions for business and customers Italy and abroad